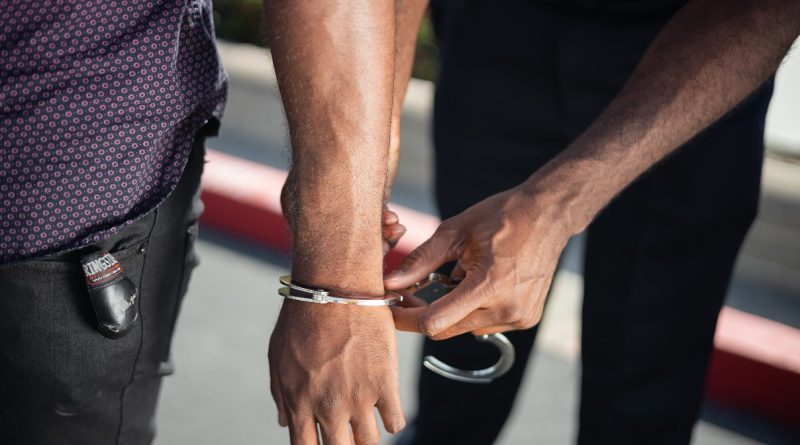
Arrest of Government Servant: Procedure, Rules and Consequences of Arrest
Introduction:
In Indian society a government job is considered as the the most safest job and a government employee is seen with huge respect, even in some government jobs a government employee get free accommodation, car, servants etc . Along with this, there are some responsibilities also on the shoulders of a government employee such as: working honestly, performing his duties with full dedication, maintaining faith of public in government , it is the duty of an employee to fulfill these responsibilities, but when an employee is failed in performing his duties , he has to face many consequences such as suspension, termination or arrest depending upon the kind of failure and reason for such failure, some cases of failure includes taking bribe for performing his duty , intentionally avoiding his duty , absent in the office during working hours, misbehaving with public, any other kind of act which is covered under I.P.C.or any other act . in this article we will cover the whole concept of Arrest of a government employee. So let’s discuss about it:
CDA rules related to employment:
CDA rules were enacted in year 1980 which means Conduct, Discipline and Appeal Rules, 1980 these rules talk about all the conducts and misconducts of an employee “Employee” means a person employed in the Company and also including employees whose services are temporarily placed at the disposal of Government or a Subsidiary or any Public Undertaking but does not include casual employee, work-charged or contingent staff or workman as defined in the Industrial Employment (Standing Orders). Act. 1964; and
(ii) Persons on deputation to the Company from Government or the Holding Company or a Subsidiary or any other public Undertaking;
Now we know about the meaning of an employee , it is important to discuss about the duties of such employee, CDA rules, 1980 defines the duties of an employee as:
Every employee of the Company shall at all times-
- Maintain absolute integrity and devotion to duty
- Keep working hard and honestly to enhance the reputation of the Company and avoid such act which do not suit a public servant.
- maintain supremacy of the Constitution and democratic values and perform his fundamental duties as explained in the constitution
- maintain high ethical standards and honesty
- Stay away from politics
- Must be fair and impartial in performing his duty
- Keep transparency and accountability to the Government
- Must be responsive to the public, especially to the weaker section of the soceity
- Behaving good with the public and avoiding misbehave
- Taking such decisions which are in the interest of general public
- Shall not take bribe or put any person under pressure to give bribe
- Shall not misuse his position
Legal consequences of arrest of government employee:
Consequences of criminal proceedings are based on three different stages i.e.
In case of FIR:
In India An FIR can be easily registered against a Government Employee on the basis of an application given by any person yet the proceedings are little different from proceedings against an ordinary person. A Government employee have immunity from direct arrest. Departmental inquiry is conducted before any action against such employee. In some cases An employee is asked to give written information about the FIR, in some cases an employee can be suspended temporarily, an employee can be demoted to the position lower than that having at present or until the inquiry is complete, the pending promotions can be either postponed or refused by the department.
In case of Arrest:
In case of an arrest the situation is different from FIR. In case of an arrest during investigation if an employee remained in custody for more than 48 hours ,he/she may be suspended temporarily, as soon as the employee gets the concession of bail, he have the right to set aside his suspension and get his service restored by the Hon’ble High Court
In case of Conviction or Acquittal:
In case of conviction or acquittal the situation is different from above two scenarios. In case of acquittal, a government employee is free from all the charges made against him and he is restored to his service, but in case of conviction the suspension is confirm and in some situation one can be terminated also but a convicted government employee too have the right to file writ in the high court for restoration of his service till the pendency of appeal against the conviction order by the trial court when he will come out on bail.
Legal consequences of arrest in case of 498A:
Section 498A of IPC talk about cruelty to wife for dowry by the husband or the family/relatives of husband, for a common man or his family arrest or charge under this section is like a stigma , in some cases the entire family has to spend some days in jail till they got the concession of bail whether regular or anticipatory. This section was inserted to save women from cruelty and to prevent the destruction of matrimonial homes but in recent times it is seen that this section is misused to harass the husband and his family.Now what will be the effect of an FIR u/s 498A if it is against a government employee:? The answer to this question is quite clear that on registration of FIR there will be no effect except the demand of information by the concerned department, if an employee is arrested under this section, he can be suspended temporarily, conviction rate in such cases is very low and there are rare cases in which an accused under this section is convicted because the matter is settled before reaching on conclusion, either the parties decide to live together or go for divorce u/s 13-b by mutual consent. in case of acquittal the accused is free and can join the service again.
Procedure for arrest of a government servant:
Section 46 of Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) ,1973 explain the process of arrest of a person as:
“To arrest a person the police officer actually need to touch or confine that person and force can also be used but there is no right to cause the death of a person who is not accused of an offence punishable with death or imprisonment for life”
The process is same for any person who is employed as a government servant, the only difference is that in some cases a government employee cannot be arrested without the saction or approval from the concerned department. In case an employee is caught red handed while taking bribe or is found indulged in such activity can be arrested directly, no permission from concerned department is required in such case.
Corruption charges against a government servant:
Under the Indian a the government employee is charged under the prevention of corruption act,1988. This act covers only the corrupt acts of a government employee who is involved in taking undue advantage of his/her position. As per section 4 of the act such cases are triable by a special judge. The accused is tried under this special act followed by Code of Criminal Procedure,1973. The special court have the power to try these cases summarily as per section 6 of the act.